CI/CD
Continuous Integration: automates code integration into a shared repository with frequent commits:
- automated build and testing
- version control
- code review processes
- faster error detection
- improved team collaboration
Plan -> Code -> Build -> Test -> Release -> Artifact -> Staging -> Production
Continuous deployment (CD)
Automates the release of every validated change directly to production.
CI/CD Tools:
- Github Actions
- Jenkins
- Azure DevOps
- mlflow
- …
DevOps
DevOps is a set of practices, principles, and cutural philosophies. It aims at bridging the gap between development and operations teams to improve collaboration, efficiency, and delivery of software applications.
MLOps: aim to streamline and automate the development, deployment, and maintenance of machine learning models in production environments.
Tools:
- Development: Git
- Release: Jenkinds, Github Actions
- Deployment: Docker
- Operation: Kubernetes
- Monitoring: Prometheus, Grafana
CI/CD in DevOps
After passing test cases:
git add .
git commit -m "your message"
git push origin mainCI/CD with Github Actions
Run pipeline when having a push/pull request the event to the main branch.
- Create virtual machine
- Clone source code
- Install packages
- Run test cases:
- Alert error
- Allow merge
name: CI/CD Pipeline
on:
push:
branches:
- main
jobs:
test:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout code
uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Set up Python
uses: actions/setup-python@v5
with:
python-version: '3.11'
- name: Install dependencies
run: |
python -m pip install --upgrade pip
pip install -r requirements.txt
- name: Test with pytest
run: |
pip install pytest
pytest app/tests/test_main.py
pytest app/tests/test_yolo_detect.pyGithub Actions variables
Variables provide a way to store and reuse non-sensitive information across multiple workflows and jobs.
env:
VERSION: '1.0.0'
jobs:
test:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Print version
run: echo "Version is $VERSION"
steps:
- name: Checkout code
uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Set up Python
uses: actions/setup-python@v5
with:
python-version: ${{ vars.PYTHON_VERSION }}
- name: Install dependencies
run: |
python -m pip install --upgrade pip
pip install -r requirements.txt
pip install mlflow=${{ vars.MLFLOW_VERSION }}Github Actions secrets
Secrets are variables defined within an organization repository, or repository environment. These secrets can be ultilized in Github Actions workflows but can only be accessed by Github Actions if they are explcitly specified in a workflow.
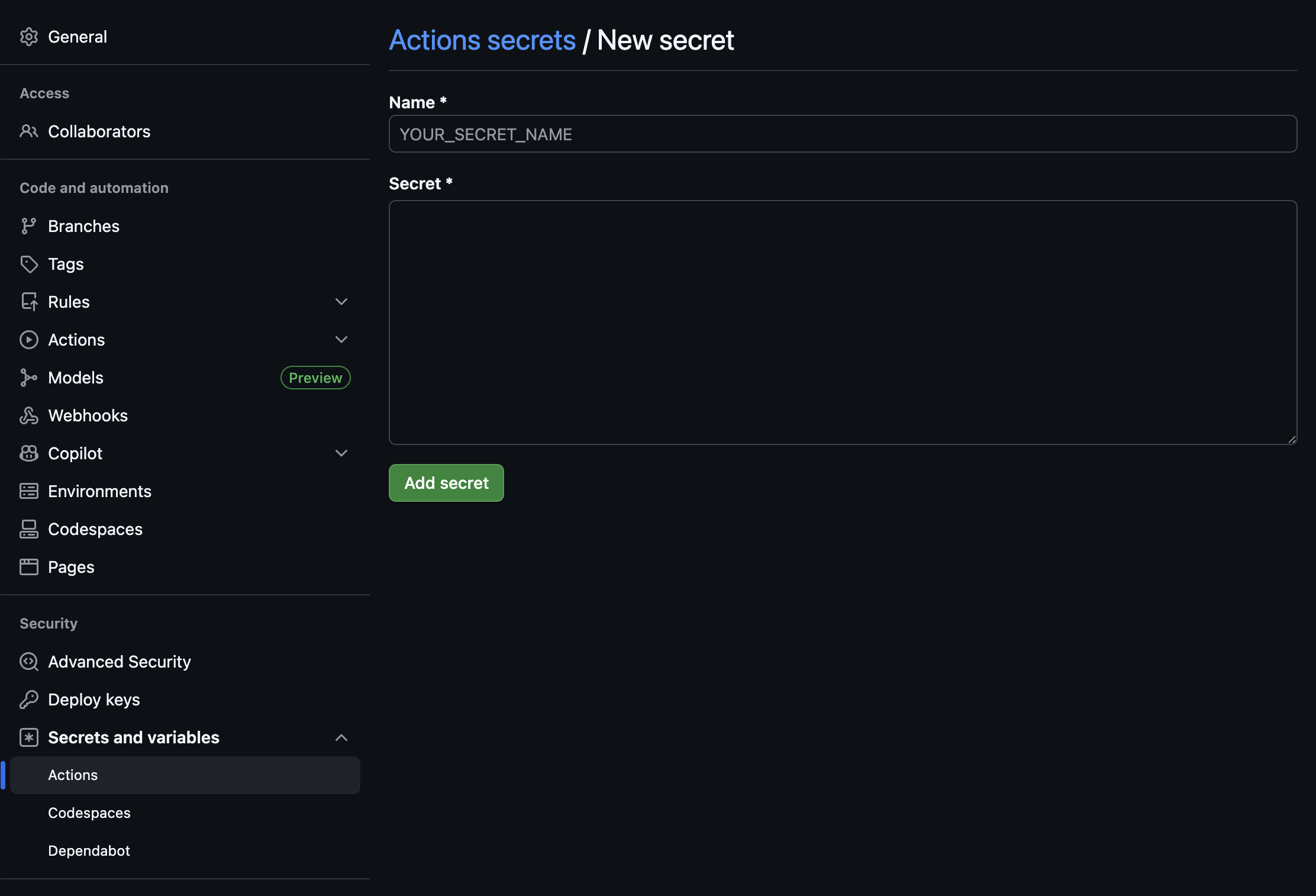
To use secrets in a workflow, you can reference them using the secrets context. For example, if you have a secret named DOCKERHUB_TOKEN, you can access it in your workflow like this:
jobs:
deploy:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Login to DockerHub
users: dockers/login-action@v3
with:
username: ${{ vars.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME }}
password: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_TOKEN }}